Before customers acquire a product—or a solution—they often compare how well it meets their needs and expectations relative to its price. Price-Value Mapping offers a structured way to analyze this comparison by visualizing the relationship between perceived value and price on a single graph.
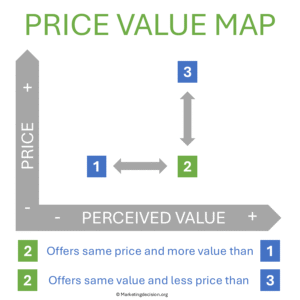
This method helps marketing and sales teams better understand how customers evaluate competing offerings and how positioning decisions can influence perceived competitiveness.
In complex purchasing decisions, sophisticated scorecards are often developed to evaluate and compare solutions from different suppliers. Customers may also assess and rank solutions based on their preferences and needs. In every case, perceived value is measured, allowing solutions to be compared against their price before a decision is made. This is precisely what the Price-Value Map enables.
Although this method is naturally used by customers, it is equally valuable for marketing and sales teams, too.
For sales, it serves as a tactical approach to assess and compare competitive offerings, helping determine pricing strategies and sales arguments.
For marketing, it supports long-term positioning decisions across a company’s range of solutions and segments.
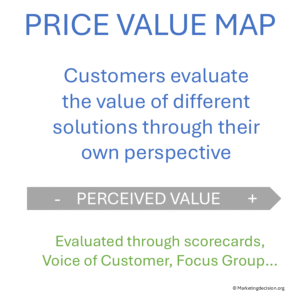 Price and value are often confused. In some cases, value can even be translated into monetary terms, but fundamentally, value represents how customers compare and rank solutions according to multiple factors. There is no need to assign a direct monetary number to a value index, as this may lead to the wrong belief that every feature can be converted into price.
Price and value are often confused. In some cases, value can even be translated into monetary terms, but fundamentally, value represents how customers compare and rank solutions according to multiple factors. There is no need to assign a direct monetary number to a value index, as this may lead to the wrong belief that every feature can be converted into price.
Value assessment is neither linear nor additive. Adding features and capabilities does not automatically increase value—some may have no relevance for certain customer segments. Even with structured evaluation scorecards, value remains subjective and fluctuates depending on sales efforts, communication effectiveness, and how benefits are perceived relative to competitors.
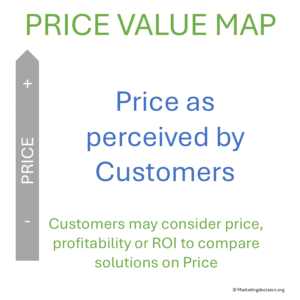
Price, by contrast, appears objective—a company decision. Yet customers also perceive cost subjectively. For some, the acquisition cost of a solution is not evaluated solely by price but by the Return on Investment (ROI) it delivers. The residual value after several years may also influence their perception.
Hence, the price dimension can also be perceived rather than purely objective. For this reason, “price” is often replaced by “perceived price”, emphasizing that evaluation depends on customer perception.
Understanding perceived value and perceived price is essential for ensuring proper market positioning, defining go-to-market strategies, and shaping effective communication.
Unlike monetary value estimation models, Price-Value Mapping keeps price and value as distinct dimensions. This separation is essential to understand how perception—rather than calculation—drives customer choices.
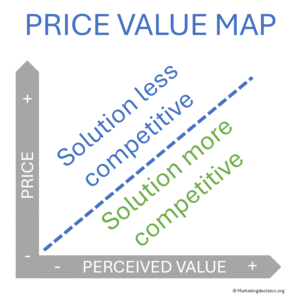 The Price-Value Map helps marketers ensure that solutions remain properly aligned with market segments and competitive dynamics. It can be applied both to current offerings and to future solution development.
The Price-Value Map helps marketers ensure that solutions remain properly aligned with market segments and competitive dynamics. It can be applied both to current offerings and to future solution development.
Price-Value Mapping allows marketing teams to visualize the relative strengths and weaknesses of existing solutions for each segment. When used effectively, it helps identify optimal positioning opportunities through packaging and pricing adjustments. Communication programs can then emphasize the differentiation factors that clearly justify the value proposition relative to competitors.
Related reading: Value Ladder — clarifying and communicating solution benefits.
Mapping current offerings is also a valuable starting point for anticipating future landscapes.
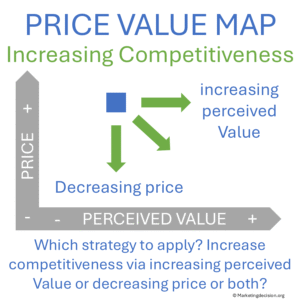
Key questions include:
What new offerings might emerge in the market?
Will they come from existing competitors or new entrants?
Are there gaps for specific customer segments?
What price dynamics are likely to appear?
With Price-Value Mapping, marketing teams can determine the best course of action for both short-term positioning and long-term development.
Scenario planning can also help anticipate competitive moves and prepare appropriate responses.
Related reading: Strategic Position Analysis Tool — evaluating market attractiveness and ability to compete.
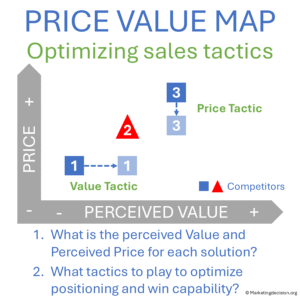 For sales teams, particularly in complex B2B projects, understanding how customers perceive the value of their solution—compared with competitors—offers a decisive advantage. One of the salesperson’s main roles is to advocate for the unique strengths of their solution and demonstrate how well it meets customer needs.
For sales teams, particularly in complex B2B projects, understanding how customers perceive the value of their solution—compared with competitors—offers a decisive advantage. One of the salesperson’s main roles is to advocate for the unique strengths of their solution and demonstrate how well it meets customer needs.
To do this effectively, it is crucial to identify what the customer values most. The Price-Value Map becomes a tactical instrument for selecting the arguments that best differentiate the offering and for countering competitive claims.
Timing is essential. Early in the sales cycle, it helps determine the customer’s budget and avoid proposing products beyond their price range.
During later stages, it supports negotiation by showing where the offering stands relative to perceived value.
Deals are often lost when solutions are viewed as overpriced compared to perceived benefits; this method helps justify pricing decisions without eroding value.
Reducing prices strategically—while maintaining configuration and value perception—is key to winning deals without weakening the overall proposition.
See also: Economic Value Estimation (EVE) — quantifying value drivers and ROI for sales argumentation.
Price-Value Mapping is most effective when applied to a specific customer segment, or in certain markets, to individual strategic accounts.
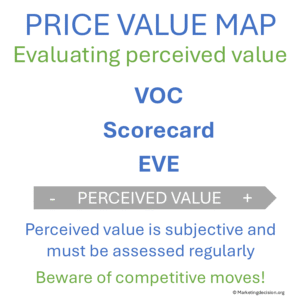
Perceived value should be measured as accurately as possible. Using a scorecard that reflects segment priorities and integrates Voice of the Customer (VOC) data is a sound approach.
However, scorecards can suggest that value is additive and linear, which does not reflect reality. Over time, they can be refined to better represent how each segment evaluates solutions.
Another option is to rely on customer evaluation methods themselves. Some organizations develop their own systems for comparing solutions. Building long-term collaborations can provide insight into how they weigh different factors—revealing which features are over- or undervalued.
Focus groups and feedback sessions are also useful in assessing perceived value and comparing alternatives.
Any approach that integrates customer input strengthens the reliability of the map.
Using the Price-Value Map effectively means identifying which arguments to emphasize in each selling situation. Certain features can increase competitiveness while allowing a higher price and margin—these tactics should be applied deliberately.

When considering price, always use the definition most relevant to the segment:
Is the purchase price or running cost more important?
Does the total cost of ownership (TCO) drive decision-making?
Should the resale value be included, especially if it enhances ROI perception?
Regular cross-functional meetings—between marketing, sales, and product teams—are essential to review positioning, adjust sales pitches, and capture market feedback.
Marketing and sales teams should discuss pricing effects, competitor movements, and shifts in customer perception to maintain alignment between pricing strategy and value communication.
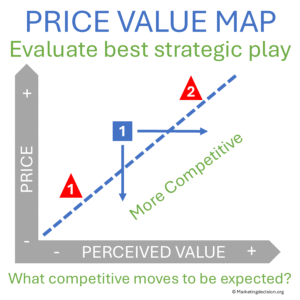 The Price-Value Map is a valuable decision-support method used by both customers and companies to clarify how price and perceived value interact in purchasing decisions.
The Price-Value Map is a valuable decision-support method used by both customers and companies to clarify how price and perceived value interact in purchasing decisions.
For marketers, it strengthens competitive positioning and portfolio management.
For sales teams, it supports persuasive argumentation and value-based negotiation.
By systematically applying Price-Value Mapping, organizations align their understanding of customer perceptions, refine pricing decisions, and enhance both marketing effectiveness and sales success.
Price-value trade-offs are meaningful only when grounded in customer motivations and perceptions. For the broader context, consult our Customer Mix analysis.
Price–Value Mapping is most meaningful when supported by clear pricing principles. For a comprehensive view of value-based pricing, visit our Value Pricing page.
Price–Value Mapping supports value selling by visualizing competitive value. For methods to communicate these insights in customer discussions, visit the Value Selling page.
Price–Value Mapping becomes clearer when grounded in the Solution Mix, which structures how solutions deliver benefits and justify price levels.
A Price-Value Map is a visual framework that plots perceived value on one axis and price on the other. It helps compare how customers view competing solutions in terms of benefits delivered relative to cost.
While perceptual maps often display brand attributes like quality or image, Price-Value Mapping focuses on the trade-off between perceived value and price. It highlights competitive imbalances and supports pricing and positioning decisions.
Price-Value Mapping is valuable during portfolio reviews, go-to-market planning, and sales negotiations. It clarifies whether a solution appears overpriced, underpriced, or well-positioned for its perceived value.
Perceived value can be captured through Voice of the Customer (VOC) data, customer interviews, or scoring models that reflect the evaluation criteria of each segment. The key is to represent the customer’s perspective rather than internal assumptions.
Yes. By mapping current offerings, teams can identify gaps in value or pricing, anticipate market changes, and design future solutions that better fit customer expectations and willingness to pay.
© marketingdecision.org
The following section may include tools, some free, some with a fee to support this site development. If you consider a tool should be presented in this section and is missing, please let us know at: contact@marketingdecision.org
© 2026 MARKETING DECISION SOLUTIONS. All Rights Reserved.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
These cookies are needed for adding comments on this website.
Stripe is a payment processing platform that enables businesses to accept online payments securely and efficiently.
Service URL: stripe.com (opens in a new window)
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)