 Putting together a detailed market forecast and then building the business plan may create a false sense of confidence in the end result.
Putting together a detailed market forecast and then building the business plan may create a false sense of confidence in the end result.
Because quantitative forecasting comes with data that seem solid and reliable—often with a significant number of decimal places—the outcome looks credible and reassuring.
Yet some significant and impactful market events may still occur, altering the plan’s validity.
Market Scenario Planning is not just about imagining alternative futures; it is about clarifying the “why” behind business decisions. By integrating scenario discussions early in the process, organizations align their strategy to what truly matters.
The key business questions are strategic:
Exploring these questions helps ensure that Scenario Planning strengthens decision-making, not only forecasting accuracy. It reconnects teams with the deeper purpose of planning—understanding why choices are made and how they support long-term value creation.
See also: Market Forecast, Qualitative Forecasting, Quantitative Forecasting and Market Visibility.
 Scenario Planning helps organizations consider alternative market situations and evaluate necessary adjustments to the business plan. A scenario represents a defined set of market conditions and events that may occur with notable impact. In practice, the objective is to understand how the business plan should be revised to address each scenario, making it more efficient, adaptable, and resilient.
Scenario Planning helps organizations consider alternative market situations and evaluate necessary adjustments to the business plan. A scenario represents a defined set of market conditions and events that may occur with notable impact. In practice, the objective is to understand how the business plan should be revised to address each scenario, making it more efficient, adaptable, and resilient.
By integrating scenario planning, companies can strengthen their business plans and enhance their ability to manage uncertainty. A well-prepared company can seize opportunities faster and respond to threats more effectively than competitors.

Scenario planning begins with a discussion about potential market events, offering a broader perspective on possible developments and their impacts.
The Qualitative Forecasting Tool proposed on this site is effective for this purpose, especially when used alongside PESTLE and Porter’s Five Forces analyses.
Encourage teams to select a few pivotal events with significant impact—positive or negative—and focus on those that could disrupt or reshape the initial draft of the business plan.

A scenario gains meaning when it is given a name and a clear description. It should portray a complete market situation, describing its key attributes and assumptions.
Much like a persona in customer segmentation, each scenario becomes tangible and shareable.
Why name scenarios?
Because clarity is essential. Everyone involved must understand what each scenario implies, ensuring consistent language across teams—even for small variants.
 Once scenarios are detailed, it becomes easier to determine how the business plan can be made more resilient.
Once scenarios are detailed, it becomes easier to determine how the business plan can be made more resilient.
For each scenario:
The goal is not to create a full plan for every scenario, but to identify vulnerabilities and adjustments that improve robustness when market conditions shift.
Introducing scenario planning late in the business-planning process may resemble destructive testing—discovering weaknesses after validation.
The optimal time is early, together with Qualitative Forecasting, when teams still have open discussions about market developments. Starting early makes Scenario Planning a testing ground for strategic ideas rather than a late-stage correction.
Related methods:PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, Risk and Opportunities Matrix, and Value Ladder Tool.
These support structured discussions about external changes, internal responses, and the strategic value of alternative scenarios.
See also: Market Presence and Strategic Position Analysis.
A common practice is to establish a baseline scenario—representing the standard market forecast—and add alternative scenarios that address plausible variations such as a sudden competitive move or an economic slowdown. This enables the company to prepare contingency plans and allocate resources more effectively.
Teams should use scenario discussions to answer the key business question:
“What if this happens—what will we do, and why?”
Market Scenario Planning is most effective when teams anchor discussions on the “why” behind decisions and continuously revisit the “so what” question to interpret market events in context. The goal is not only to describe what might happen, but to determine why it matters and what actions it calls for.

Start early, alongside qualitative work. Initiate scenarios with Qualitative Forecasting to gather frontline signals and probabilities while ideas are fresh.
Pair external and competitive lenses. Combine PESTLE Analysis and Porter’s Five Forces to explore how macro trends and competitive shifts interact.
Name and limit scenarios. Keep a small number—baseline, stress, and upside—and assign clear names to ensure shared understanding.
Document risks and opportunities per scenario. Capture exposure, likelihood, and recommended actions using the Risks & Opportunities Tool so discussions remain concrete.
 Ask the “so what” at every step. When a potential event is identified—like a competitor’s new product or a regulatory shift—pause to ask:
Ask the “so what” at every step. When a potential event is identified—like a competitor’s new product or a regulatory shift—pause to ask:
So what does this mean for our company, our customers, and our plan?
This simple but powerful question anchors Scenario Planning in relevance, clarifying which impacts deserve attention and how the plan should evolve.
Make the “why” explicit. Use the Value Ladder to explain why specific responses add value, linking customer motivations to solution design and perceived value.
Link scenarios to investment choices. Connect insights with Strategic Position Analysis and Market Presence to align resources, go-to-market priorities, and development focus.
Maintain a living signal log. Update scenario watchpoints regularly through Market Visibility, transforming weak signals into timely strategic reactions.
Close the loop. After events occur, review what happened, so what the implications were, and why the company’s reaction worked or needs adjustment.
Scenario planning — Wikipedia — an extensive overview of definitions, processes, and examples.
Qualitative Forecasting Tool (Excel) — document market events, probabilities, and impacts; visualize results with built-in charts.
Symbol Text Generator — convert findings into short, symbol-enhanced statements for presentations and workshops.
Strategic Position Analysis — compare solutions by ability to compete and market attractiveness to inform investment choices.
Market Presence — evaluate your presence across market segments to guide resource allocation and strategic focus.
 Scenario Planning is not a forecasting exercise but a strategic approach to make a business plan more resilient and better aligned to the market environment.
Scenario Planning is not a forecasting exercise but a strategic approach to make a business plan more resilient and better aligned to the market environment.
It enables faster adjustments to external events, early preparation for risks, and sharper focus on emerging opportunities.
Utilize scenario planning to identify vulnerabilities, opportunities, and the underlying reasons why plans must evolve.
Rather than building multiple business plans, strengthen one adaptive plan capable of handling change.
Scenario planning draws heavily on customer-driven insights and expected behavioral shifts. For these foundational elements, review our Customer Mix analysis.
Scenarios become more meaningful when grounded in how markets evolve. Refer to Market Mix for the structural view supporting scenario discussions.
Market Scenario Planning is a structured approach that helps organizations prepare for uncertain market conditions by defining and analyzing alternative market situations. It strengthens confidence in forecasts and improves the adaptability of business plans.
It enables teams to anticipate risks, seize opportunities, and align decisions with long-term priorities—keeping focus on why strategies matter rather than only what to do.
Ideally at the same time as Market Forecasting, before the business plan is finalized, so that strategic alternatives are explored early.
By testing assumptions against multiple possible futures, teams recognize limitations in data and reinforce confidence that their plan can adapt to change.
Common tools include PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, Qualitative Forecasting, and the Risks and Opportunities Framework. Each supports structured thinking on how scenarios affect business priorities.
Usually one baseline plus two or three alternatives—optimistic and pessimistic—to balance realism with manageability.
It helps clarify why certain actions matter by linking decisions to possible outcomes. Teams develop shared understanding and become more agile when facing change.
© marketingdecision.org
Scenario planning challenges teams on multiple levels: first, in selecting and developing meaningful scenarios, and second, in determining the appropriate company strategy for each scenario.
To select relevant scenarios, teams should evaluate both the probability and potential impact of each option, ultimately agreeing on a few scenarios that are sufficiently distinct and insightful—even if actual outcomes differ. Tools such as the Decision Project Prioritization tool can facilitate the comparison and selection process, while the Value Ladder can help teams discuss and compare the underlying reasons why certain scenarios are important.
A common approach is to establish a baseline scenario—typically the standard market estimate if scenario planning were not used—and then add a few alternative scenarios that address plausible, even if extreme, variations. This process enables the company to better prepare for uncertainty and develop contingency plans, without the need to create a full marketing plan for every scenario.
Determining the company’s strategy for each scenario may involve tools described in the various marketing mix chapters, such as those focused on solution, placement, promotion, and communication.
The following section may include tools, some free, some with a fee to support this site development. If you consider a tool should be presented in this section and is missing, please let us know at: contact@marketingdecision.org
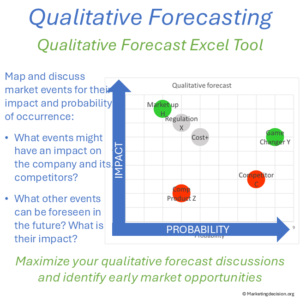 Qualitative forecast is essential to address topics that are not easily measurable. Sales, Marketing, Quality and other functions working with customers can provide valuable inputs for qualitative forecasting.
Qualitative forecast is essential to address topics that are not easily measurable. Sales, Marketing, Quality and other functions working with customers can provide valuable inputs for qualitative forecasting.
This Excel tool can be utilized across multiple instances with various teams. Its primary purpose is to document events, assign probability of occurrence, and evaluate their impact on a scale ranging from 0 to 9. This structured approach facilitates productive discussions within the teams. The tool also provides a graphical representation with multiple options.
 The Symbol Text Generator is an Excel tool that helps synthesize key ideas into short, crisp messages with the aid of symbols. Whether summarizing findings after a workshop or preparing a presentation, conveying insights clearly is essential. Given the significant volume of data from a Porter’s Competitive Analysis or PESTLE, using symbols and colors can enhance communication and presentation.
The Symbol Text Generator is an Excel tool that helps synthesize key ideas into short, crisp messages with the aid of symbols. Whether summarizing findings after a workshop or preparing a presentation, conveying insights clearly is essential. Given the significant volume of data from a Porter’s Competitive Analysis or PESTLE, using symbols and colors can enhance communication and presentation.
Crafting precise text with meaningful symbols can be time-consuming. This tool simplifies the process by enabling users to add symbols at the beginning or end of sentences and select colors aligned with their company’s branding. In addition to pre-formatted pages for Porter’s and PESTLE analyses, it includes a free-text page for general use. Simply prepare your text with symbols, copy and paste it into your presentation—it’s that easy.
© 2026 MARKETING DECISION SOLUTIONS. All Rights Reserved.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
These cookies are needed for adding comments on this website.
Stripe is a payment processing platform that enables businesses to accept online payments securely and efficiently.
Service URL: stripe.com (opens in a new window)
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)