From assessing channel distribution and performance to defining the optimal go-to-market strategy, headcount, and e-commerce coverage, the review of Place Mix concludes with a critical dimension: Sales Enablement.
Sales enablement is about aligning the entire organization — not only the sales team — to address markets effectively, identify opportunities, and close deals efficiently. It involves implementing the tools, processes, and mechanisms that make business execution seamless and data-driven. CRM systems, sales operating mechanisms, and all back-office functions, from shipment to installation, form the backbone of a well-enabled sales ecosystem.
When these elements work together, they build an organization capable of responding quickly to customer needs, improving collaboration, and driving measurable results. Performance and profitability ultimately stem from the collective efforts of individuals across front- and back-office functions — coordinated through effective enablement.
Sales enablement ensures that strategy, tools, skills, and incentives translate into consistent execution in the field.
 Sales enablement bridges strategy and execution. It ensures that the company’s objectives are translated into actionable tools and behaviors that strengthen field performance.
Sales enablement bridges strategy and execution. It ensures that the company’s objectives are translated into actionable tools and behaviors that strengthen field performance.
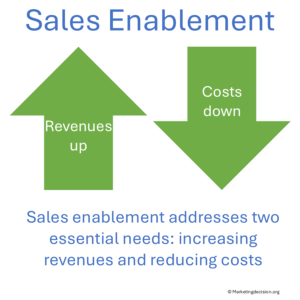
When well structured, enablement boosts revenue growth and cost efficiency — the two essential levers of profitability.
It goes beyond short-term sales targets and creates a sustainable system that improves both customer experience and organizational agility.
Creating an enablement function requires cross-functional collaboration. A strong team will include people experienced in marketing, commercial operations, quality, and data management. These professionals connect information across multiple sources to identify growth opportunities and operational bottlenecks.
Several improvement paths can be pursued in parallel — from CRM design and process optimization to training, marketing alignment, and go-to-market activation. When managed coherently, these initiatives reinforce each other and accelerate overall performance.
 A CRM that merely records activities and generates reports misses its true purpose. A well-designed CRM must connect information streams across all company functions — marketing, manufacturing, service, and logistics — ensuring everyone works from the same, reliable data.
A CRM that merely records activities and generates reports misses its true purpose. A well-designed CRM must connect information streams across all company functions — marketing, manufacturing, service, and logistics — ensuring everyone works from the same, reliable data.
The mission of a CRM is transparency. When sales information flows openly, decisions become faster and better. This requires consistent reporting discipline and a company culture that values data integrity.
Hidden or incomplete information damages trust and creates poor decisions. Building a CRM that people trust begins with correcting data errors early and training users to “do it right the first time.” Avoid multiplying filters or alternative dashboards that mask problems. Instead, ensure everyone can access reliable, shared data — the core of effective enablement.
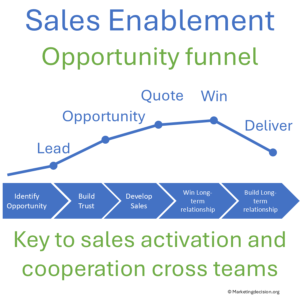 A robust sales funnel clarifies each step from opportunity identification to deal closure. It helps marketing, pricing, support, manufacturing, and logistics coordinate their actions and anticipate needs at every stage.
A robust sales funnel clarifies each step from opportunity identification to deal closure. It helps marketing, pricing, support, manufacturing, and logistics coordinate their actions and anticipate needs at every stage.
The best salespeople engage customers before opportunities formally exist. Early conversations allow them to influence needs and perceptions, often when competition has not yet shaped the debate. Entering discussions early is a decisive advantage.
Monitoring funnel quality is equally important. Individuals who rarely update their pipeline may appear to have high win rates, but often this is due to under-reporting. To obtain a realistic view, compare CRM data with external market information. Use a waterfall model to estimate potential: market → opportunities → wins. This approach works for both direct and indirect sales channels.
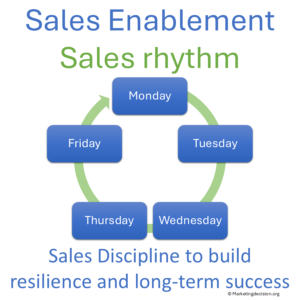
A consistent sales rhythm creates alignment and discipline across the organization. Regular one-to-one and team meetings give structure to performance reviews, opportunity discussions, and knowledge sharing.
One-to-one meetings should focus on pipeline health, key deals, training needs, and short-term priorities. They also help managers support individuals through coaching and early assistance on strategic prospects.
Team reviews are opportunities to share insights about markets, competitors, marketing campaigns, and new product launches. Keep sessions concise and purposeful — several short, focused meetings are more effective than one long session.
Sales training remains a cornerstone of enablement. Yet, it is most effective when integrated into daily routines rather than handled as a stand-alone initiative. One-to-one meetings and team reviews are perfect moments to share best practices, address challenges, and reinforce desired behaviors.
Structured coaching programs, mentoring systems, and peer-learning initiatives all contribute to building collective knowledge and sustaining long-term performance.
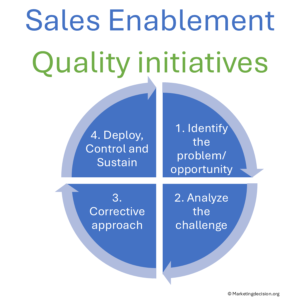 Improving quality across processes directly impacts profitability. Non-quality, rework, or internal inefficiencies waste time and limit customer-facing activities.
Improving quality across processes directly impacts profitability. Non-quality, rework, or internal inefficiencies waste time and limit customer-facing activities.
Quality initiatives within sales enablement aim to simplify workflows, eliminate friction, and free up time for selling.
To be effective, these initiatives must be led by people capable of supporting both sales and support functions — managing data, solving operational issues, and aligning teams. The objective is simple: let salespeople spend more time with customers, not in internal loops.
 Sales enablement must evolve continuously. Measure results to understand what works and what needs refinement. Common indicators include funnel conversion rates, time to productivity for new hires, content utilization, average deal size, and win rates by segment.
Sales enablement must evolve continuously. Measure results to understand what works and what needs refinement. Common indicators include funnel conversion rates, time to productivity for new hires, content utilization, average deal size, and win rates by segment.
A data-driven review process ensures that investments in tools, training, or marketing alignment deliver measurable impact. By comparing current outcomes with initial objectives, companies can make informed decisions on where to improve next.

Numerous definitions of sales enablement can be found online. Each reflects the company’s focus — CRM vendors stress data and tools, consulting firms emphasize processes, and technology platforms highlight AI integration.
Below are several valuable references covering complementary perspectives on sales enablement, training, and process optimization:
Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Quick and practical overview of how to use data and AI to strengthen sales enablement across teams.
Gartner – In-depth concepts and strategic frameworks that connect enablement with broader commercial performance.
Zendesk – A comprehensive presentation of how sales enablement extends beyond sales to include service and support functions.
Salesforce – Defines sales enablement as a continuous process to equip and train salespeople for better engagement.
RevenueGrid – Miller Heiman Methodology – A classic structured approach to managing complex sales and multi-decision-maker deals.
Highspot – Insightful overview of enablement best practices, focusing on content, training, and digital collaboration tools.
Predictable Revenue – Detailed examples of metrics and KPIs to evaluate the effectiveness of your sales enablement strategy.
LinkedIn Pulse – Sales Rhythm – Useful perspective on how structured meeting cadences improve sales rhythm and organizational focus.
When exploring the web, remember that “sales enablement” can take many forms depending on the author’s point of view.
While some describe it narrowly as sales activation — focusing on high-probability customers and short-term wins — a broader understanding connects it to long-term company strategy and customer value creation.
Sales enablement is more than a sales initiative — it is a company-wide mission. It connects front-office and back-office teams, aligning every function toward customer success.
Approaching enablement as part of corporate strategy ensures that all departments contribute to revenue generation and customer satisfaction. Detect issues early, act decisively, and maintain alignment across teams.
The most successful organizations are those where sales excellence reflects company excellence.
Sales programs become more effective when anchored in a deep understanding of customer needs and motivations. For these foundational insights, visit our Customer Mix page.
Sales enablement requires structured solution definitions. Explore our Solution Mix page for the foundational framework.
Sales enablement programs are most effective when centered on clear value messages. Visit our Value Selling page to see how value is structured and communicated.
Enablement efforts have greater impact when aligned with a coherent Go-to-Market model. See Place Mix Strategy for the overarching structure.
Sales enablement is the structured process of aligning people, tools, and processes to help sales teams perform more effectively. Within company strategy, it ensures that marketing, operations, and support functions all contribute to revenue creation by giving sales the right information, content, and systems to succeed. It turns strategy into execution.
Sales operations focus on structure and data, while training develops skills. Sales enablement integrates both — it connects strategy, operations, and learning into one system that supports performance in the field. Enablement builds the ecosystem that allows sales operations and training to deliver consistent business impact.
A CRM system is the information backbone of enablement. It enables transparency, data accuracy, and collaboration across teams. When used properly, CRM tools help companies move beyond reporting to real-time decision-making, allowing marketing, sales, and service to act in alignment.
Typical metrics include funnel conversion rates, win ratios, deal size, time-to-productivity for new hires, and content utilization by the sales team. More advanced organizations also track efficiency gains — such as time freed from internal tasks — to quantify the full value of enablement investments.
Because customer experience depends on every function that touches the buyer journey — from marketing to service. Sales enablement creates alignment across these teams, making the organization faster, more consistent, and more responsive to customer needs. In essence, sales enablement is company enablement.
© marketingdecision.org
Sales enablement should be viewed as a continuous journey, not a one-time project. Review previous plans, assess progress against initial goals, and adjust for future growth.
Explore tools and resources related to enablement on our Marketing Decision Webshop — some are free, others available for purchase to support ongoing site development. Be sure to analyze the Sales benchmark, assess progress achieved since its initial development, and consider future improvements needed for continued growth.
The following section may include tools, some free, some with a fee to support this site development. If you consider a tool should be presented in this section and is missing, please let us know at: contact@marketingdecision.org
© 2026 MARKETING DECISION SOLUTIONS. All Rights Reserved.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
These cookies are needed for adding comments on this website.
Stripe is a payment processing platform that enables businesses to accept online payments securely and efficiently.
Service URL: stripe.com (opens in a new window)
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)