Go-to-market choices are among the most structuring decisions a company makes. They determine how solutions reach customers, how teams are organized, how resources are allocated, and how the company operates on a daily basis. Once in place, these decisions are difficult to reverse.
The Place / Go-to-Market Strategy page exists to support this moment of collective commitment. It helps you approach go-to-market decisions deliberately: how to choose channels, design coverage models, and align organizational structures with strategic intent and market realities.
In an AI-assisted world, data and benchmarks can inform go-to-market options. This page focuses on what remains Human: judgment, alignment, and the responsibility to commit people, budgets, and time to a chosen way of operating in the market.
 The Place Mix Strategy defines how products and solutions that meet customer needs and expectations are made available to the market. It is the distribution strategy that ensures the company’s value reaches customers efficiently, profitably, and consistently across all channels.
The Place Mix Strategy defines how products and solutions that meet customer needs and expectations are made available to the market. It is the distribution strategy that ensures the company’s value reaches customers efficiently, profitably, and consistently across all channels.
Every interface between the company and its customers contributes to “place.” This includes sales representatives, service and support teams, and participants in distribution networks. The scope extends to all customer-facing roles, such as influencers, CEOs, and digital platforms — including e-commerce — which have become essential for ensuring effective market coverage and accessibility.
Many operational questions arise when addressing the Place Mix Strategy:
These “what” and “how” questions are valid and necessary. However, without being anchored in the company’s strategic intent — the “why” — such actions risk being misaligned or ineffective. The “why” serves as a compass for optimizing distribution and go-to-market strategy. When ambiguity or implementation challenges arise, returning to this core intent helps clarify objectives, identify priorities, and ensure alignment across marketing, sales, and distribution decisions.

A further difficulty lies in the diversity of metrics used by marketing, sales, and support teams. Many indicators reflect internal performance (such as pipeline health or conversion ratios) but fail to measure alignment with company goals. To avoid misinterpretation, it is essential to establish a shared set of strategic objectives guiding the go-to-market approach.
Moreover, “place” cannot be optimized in isolation. It must reflect market dynamics, customer segments, solution value, and promotional strategy. Market and customer insights help identify the most profitable and scalable segments, while product and promotional strategies determine how to reach and serve them effectively.
For these reasons, it’s crucial to continuously ask strategic “why” questions such as:
These guiding questions help anchor every decision in the company’s broader priorities. They also ensure that actions related to optimizing placement — such as channel design, headcount allocation, territory balance, skills development, and sales enablement — remain coherent and purposeful.
To capitalize on every market opportunity as early and efficiently as possible, companies must review how the Place Mix Strategy supports their go-to-market model. This means regularly assessing how well their sales organization meets business needs and aligns with strategic objectives — the company’s “why.”
The following chapters explore how to evaluate, design, and strengthen each dimension of the Place Mix Strategy — from channel management and headcount to territory design, competencies, and enablement — ensuring that every link between the company and its customers contributes to both market coverage and profitable growth.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of a sales organization requires a thorough review of several aspects of the go-to-market strategy. The goal goes beyond identifying operational pain points; it is about assessing how effectively the sales organization meets business needs and aligns with company priorities — the “why.”
When developing a marketing plan, factors such as market trends, customer needs and expectations, and product offerings must be considered.
These shape the go-to-market approach and influence the company’s ability to achieve growth and profitability. Developing an updated strategy involves aligning internal strengths and weaknesses with both business priorities and market needs.
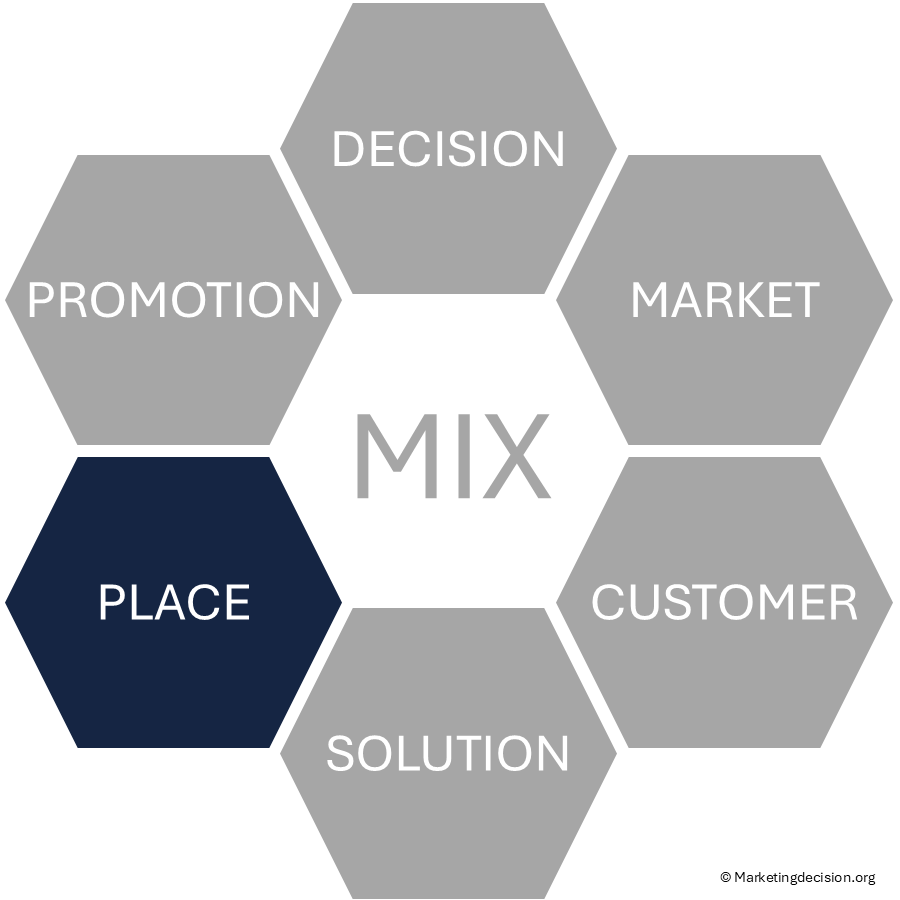
Benchmarking or assessing your go-to-market approach can focus on six core components:

The objective of this assessment is to:
Such an assessment also provides an opportunity to examine the competitive landscape. For those exploring alternative distribution channels, valuable insights can be gained by studying market dynamics and observing how competitors organize their sales and distribution models.
In summary, a comprehensive assessment of the sales organization builds a clearer understanding of where the company stands today, where it needs to be, and how to get there. It creates a foundation for cross-functional alignment and strategic prioritization — all essential to improving performance across every component of the Place Mix Strategy.
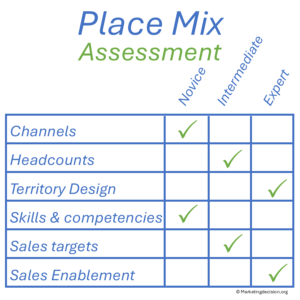
Multiple channels can be considered — whether direct or indirect, through e-commerce, dealers, or distributors — individually or in combination, depending on business needs. Each channel offers distinct advantages and limitations in terms of cost, flexibility, control, and ability to reach targeted customer segments.

Benchmarking the current go-to-market model means challenging the existing approach and exploring potential future models. What benefits could they bring? How would they better address your critical needs and strategic priorities?
This step is essential before any other effort to optimize sales operations, grow revenue, or enhance profitability. It establishes a factual understanding of what works, what doesn’t, and where changes can create measurable value.
A strong channel strategy balances coverage, efficiency, and control. While expanding into new channels can accelerate growth, it may also dilute influence over customer relationships or introduce complexity in coordination and pricing. Hence, careful evaluation and testing are crucial before large-scale deployment.
By clarifying the role of each channel and its contribution to the overall go-to-market model, companies can ensure their Place Mix Strategy directly supports both customer needs and company objectives.

Whether direct or indirect, adding a salesperson is both a risk and an opportunity. Salespeople are rarely interchangeable, even if some organizations attempt regular territory rotations.
Performance differences among salespeople stem not only from their skills and competencies but also from their workload. Each individual faces the same time constraints, and excessive travel or administrative tasks reduce the time available for customer engagement and sales discussions.
Increasing sales headcount can help reduce territory size, improve customer coverage, and expand overall team capacity. However, this expansion comes at a cost. That’s why developing tools that free up time for sales teams is essential. Effective CRM solutions and streamlined processes play a critical role in boosting productivity and efficiency.
Balancing sales headcount is ultimately about aligning resources with opportunity. Expanding the team without improving structure or tools can lead to inefficiencies, just as reducing staff without proper analysis can limit growth. A thoughtful balance between cost and performance ensures that each salesperson contributes optimally to market reach and profitability.
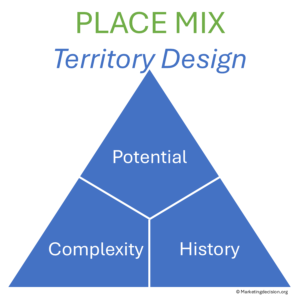
Ensuring that sales territories are appropriately sized and balanced is a continuous challenge. Market opportunities evolve, team members may be reassigned, and new accounts constantly emerge. Maintaining equitable coverage while optimizing performance requires ongoing attention.
In an ideal world, all territories would have equal potential, complexity, and history. In reality, these dimensions vary widely and must be assessed carefully:
Measuring these metrics locally enables organizations to compare and optimize territory coverage. It also helps define local performance indicators and monitor growth in specific segments.
Unbalanced territories — where some salespeople manage large, easy-to-prospect areas while others handle smaller, more competitive ones — create inefficiencies. Correcting territory and workload misalignment often has greater impact on performance than simply adjusting headcount.

Developing sales competencies is essential to building successful and resilient teams.
It begins with sales meetings, where experienced professionals share best practices and tactics, and continues through joint marketing and training sessions that strengthen knowledge, positioning, and technique.
Without adequate training, salespeople rely on trial and error — a costly approach that leads to missed opportunities. Identifying training needs early is crucial to improving win rates and profitability.
Analyzing past wins and losses reveals where deals were lost due to insufficient product knowledge, weak messaging, poor positioning, or failure to identify decision-makers. The cumulative effect of these missed opportunities represents significant lost revenue and underscores the value of continuous skills and competency development within the Place Mix Strategy.
 Managing and setting sales targets is critical to sustaining performance. When well-designed, targets motivate teams, align individual goals with company strategy, and support balanced growth. When poorly defined, they can lead to frustration and turnover.
Managing and setting sales targets is critical to sustaining performance. When well-designed, targets motivate teams, align individual goals with company strategy, and support balanced growth. When poorly defined, they can lead to frustration and turnover.
Sales incentives must be fair, transparent, and aligned with both company goals and local market realities.
Unbalanced approaches create risk:
To prevent such imbalances, territory design and target setting must be tightly linked. Fair and achievable targets create a sense of ownership and engagement across the organization, transforming objectives into collective drivers of success.

Sales enablement equips sales teams — and the entire organization — to effectively address the market, identify opportunities, and close deals. It involves implementing tools, processes, and mechanisms that streamline operations and strengthen collaboration.
CRM systems, sales frameworks, logistics, and back-office support all form part of the sales ecosystem. Measuring sales performance means assessing not just individual efforts but the collective efficiency of this ecosystem.
In essence, sales enablement is company enablement. It ensures that the entire organization — marketing, sales, service, and operations — works in sync, aligning around customer value and business performance. A strong Place Mix Strategy integrates enablement as a core driver of productivity, agility, and customer success.
Within the marketing mix, Place is where expectations for sales management and leadership are highest. Managing commercial challenges, motivating teams, and maintaining the balance between front-office engagement and back-office support are key responsibilities.
Regularly reviewing the go-to-market model helps identify gaps in sales deployment, collaboration, and support. Addressing these issues requires a systematic, cross-functional approach — led by strong sales leadership.
Ultimately, it is the leadership skills of sales managers that determine how effectively the human side of sales is managed. Balancing territory complexity, workload, and opportunity requires dedicated support from marketing and sales operations experts, ensuring fair conditions and a consistent one face to the customer across all touchpoints.
Go-to-market choices inevitably translate into Human behavior. They shape how teams collaborate, how trust is built internally, and how the company presents itself to customers through a consistent and credible “one face.” While analysis and AI-assisted insights can inform these choices, alignment, commitment, and coherence remain deeply Human responsibilities. This is why Place decisions matter: they turn strategy into shared action.
A well-executed Place Mix Strategy aligns leadership, structure, and customer experience — creating unity, trust, and long-term business health.
Your feedback and specific needs are greatly valued. Feel free to reach out to us at contact@marketingdecision.org if you have any questions, special requirements, or recommendations.
© marketingdecision.org

Benchmarking the go-to-market approach is a cornerstone activity when evaluating the current sales organization and defining future strategies. It provides a clear and structured view of the AS-IS situation before any transformation begins and establishes a baseline for comparing targeted and achieved results once changes are implemented.
Through a structured analysis, the Channel Benchmark acts as a revealer of both organizational strengths and improvement needs, helping clarify the “why” behind transformation before execution planning. It brings focus to priorities, ensures alignment with company objectives, and facilitates collaborative discussions across teams.
This approach enables companies to evaluate front- and back-office contributions, compare alternative go-to-market models, and extract learning insights for future channel or sales organization improvements.
Ultimately, benchmarking the Place Mix Strategy ensures that distribution, sales, and support functions evolve in step with market opportunities and business priorities.

Defining an effective Channel Strategy is a key step in shaping the company’s overall Place Mix Strategy and Go-to-Market approach.
Each channel — whether direct, indirect, e-commerce, or through distributors — brings unique advantages and trade-offs in cost, flexibility, and reach. The challenge is to align channel choices with company priorities, customer needs, and long-term profitability.
A well-structured Channel Strategy goes beyond deciding how products reach markets — it clarifies why specific paths are chosen and how they support the company’s strategic objectives. Benchmarking the current channel setup (AS-IS) helps identify what works, what requires adjustment, and which future-state (TO-BE) models could deliver better performance.
Balancing coverage, control, and collaboration across channels ensures that every sales route contributes efficiently to market access and brand consistency.
An effective Channel Strategy integrates direct, indirect, and digital options in a complementary way, creating a flexible and scalable distribution framework that supports sustained growth.
 Optimizing Go-to-Market Headcount is one of the most strategic decisions in a company’s Place Mix Strategy. It determines how resources are deployed across sales, marketing, and support functions to balance market coverage, profitability, and operational efficiency.
Optimizing Go-to-Market Headcount is one of the most strategic decisions in a company’s Place Mix Strategy. It determines how resources are deployed across sales, marketing, and support functions to balance market coverage, profitability, and operational efficiency.
Organizations often weigh two contrasting models — large structures offering broad presence versus leaner teams focused on high-margin segments and flexibility. The right approach depends on market potential, competitive intensity, and business priorities.
Headcount decisions are not linear: doubling team size does not double market share. As organizations grow, efficiency gains diminish while structural costs increase. This is why capacity planning must integrate profitability, flexibility, and alignment to opportunity — assessing not only how many people are needed but where they will have the greatest impact.
Scenario planning and data-driven analysis help leadership test alternatives before committing to major changes, ensuring that resources are aligned with market opportunities and that growth ambitions remain sustainable.

Effective Sales Territory Design is at the heart of every strong Place Mix Strategy. It ensures that salespeople are aligned with market opportunities in a way that balances potential, complexity, and fairness. Structured methods now make it possible to size and assign territories objectively, allowing each salesperson to access a fair share of the market while maintaining motivation and performance.
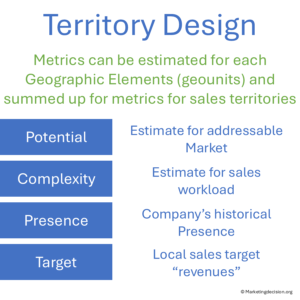
Local metrics play a critical role in territory optimization. By analyzing market potential, complexity, presence, and targets, companies can identify where opportunities are being missed or where workloads are uneven. CRM and geomarketing data bring essential visibility into these dynamics, supporting better-informed adjustments.
Well-designed territories drive engagement and efficiency — unbalanced ones cause lost revenue and turnover. Aligning the sales organization to market realities through transparent, flexible, and sustainable territory design is therefore a key success factor for growth and long-term business health.
 Developing sales competencies and strengthening individual and team skills are central to every Place Mix Strategy. Sales enablement is not only about tools and processes — it’s about people, their ability to grow, collaborate, and translate expertise into performance.
Developing sales competencies and strengthening individual and team skills are central to every Place Mix Strategy. Sales enablement is not only about tools and processes — it’s about people, their ability to grow, collaborate, and translate expertise into performance.
When competencies are clearly defined and nurtured, sales organizations become more agile, capable of responding to opportunities, managing complexity, and creating lasting customer value. Skills and competencies form the foundation of sales enablement, linking human capability to measurable business results.

Continuous learning — both formal and informal — is key. Reviewing sales situations, sharing lessons, and mentoring across teams help transform individual strengths into collective excellence.
The most effective sales organizations recognize that development is ongoing: strengthening what already works, addressing needs for growth, and aligning people’s talents with business priorities.
 A Sales Competency Model provides the structure that connects skills development with company strategy. It defines what good performance looks like, clarifies expectations, and ensures that training, coaching, and recruitment all align with business objectives.
A Sales Competency Model provides the structure that connects skills development with company strategy. It defines what good performance looks like, clarifies expectations, and ensures that training, coaching, and recruitment all align with business objectives.
By translating strategy into specific, measurable capabilities, the model builds consistency across teams and promotes fairness in evaluation. It links individual learning to collective performance, ensuring that every improvement in capability supports business growth.
Within the Place Mix Strategy, the competency model serves as a foundation for sales enablement — turning people development into a continuous process that strengthens alignment between talent, execution, and market objectives.
It is not just a framework; it is the company’s definition of sales excellence in action.

A well-designed Sales Compensation Plan aligns individual motivation with company strategy, turning targets into powerful drivers of performance. Clear, measurable, and fair objectives are the foundation of every effective plan — they sustain motivation, build trust, and help sales teams focus on what matters most.
When sales targets are well set, they balance ambition and realism, ensuring that both individual and company success move in the same direction. In contrast, poorly designed plans can create frustration, inequity, and turnover.

An effective plan combines transparent metrics, territory fairness, and performance-based incentives. Bonuses and accelerators reward success, while safeguards maintain balance and prevent unintended behaviors. Continuous monitoring and open dialogue with sales teams ensure the plan adapts to market fluctuations and evolving business goals.
In the context of the Place Mix Strategy, the compensation plan is the final activation lever — translating market opportunity and go-to-market strategy into tangible, motivated sales execution.

Sales Enablement is the connecting thread between strategy and execution in the Place Mix Strategy. It ensures that the entire organization — not only the sales team — works in sync to address markets effectively, identify opportunities, and close deals efficiently.
Enablement integrates tools, processes, and collaboration mechanisms that transform business execution into a coordinated, data-driven system. CRM platforms, operational processes, and back-office functions all contribute to building a responsive, high-performing sales ecosystem.
When these elements work together, they create a company-wide rhythm — improving agility, transparency, and profitability.
Ultimately, sales enablement reflects how well the organization learns, collaborates, and aligns around customer value. A strong enablement culture drives sustainable sales excellence and long-term business growth.

This website focuses on the marketing mix and its key decision areas. Each category includes links to detailed methods, with some offering related tools available for purchase in our webshop. For easy navigation, use the main menu in the header to explore the marketing mix framework and methods. To go directly to the webshop, select the Shop menu in the header or click the link below. You can also browse by category.
© 2026 MARKETING DECISION SOLUTIONS. All Rights Reserved.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
These cookies are needed for adding comments on this website.
Stripe is a payment processing platform that enables businesses to accept online payments securely and efficiently.
Service URL: stripe.com (opens in a new window)
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)